The 5-Level Strategic Fluency Ladder
Most professionals plateau at strategic mediocrity without realizing it. Francis Wade reveals the five-level Strategic Fluency Ladder that separates executives who merely use strategy vocabulary from those who genuinely think strategically.
Ep 26 - Seth Godin - Stuck in Stale Strategy? Seeing Systems Which Hold You Back
Seth Excerpt
A Plan is Not a Strategy
In this masterclass from Harvard Business Review, Roger Martin—former dean of the Rotman School of Management at the University of Toronto and one of the world's most influential strategic thinkers—delivers a crystal-clear explanation of why most organizations confuse planning with strategy, and why that confusion guarantees mediocrity.
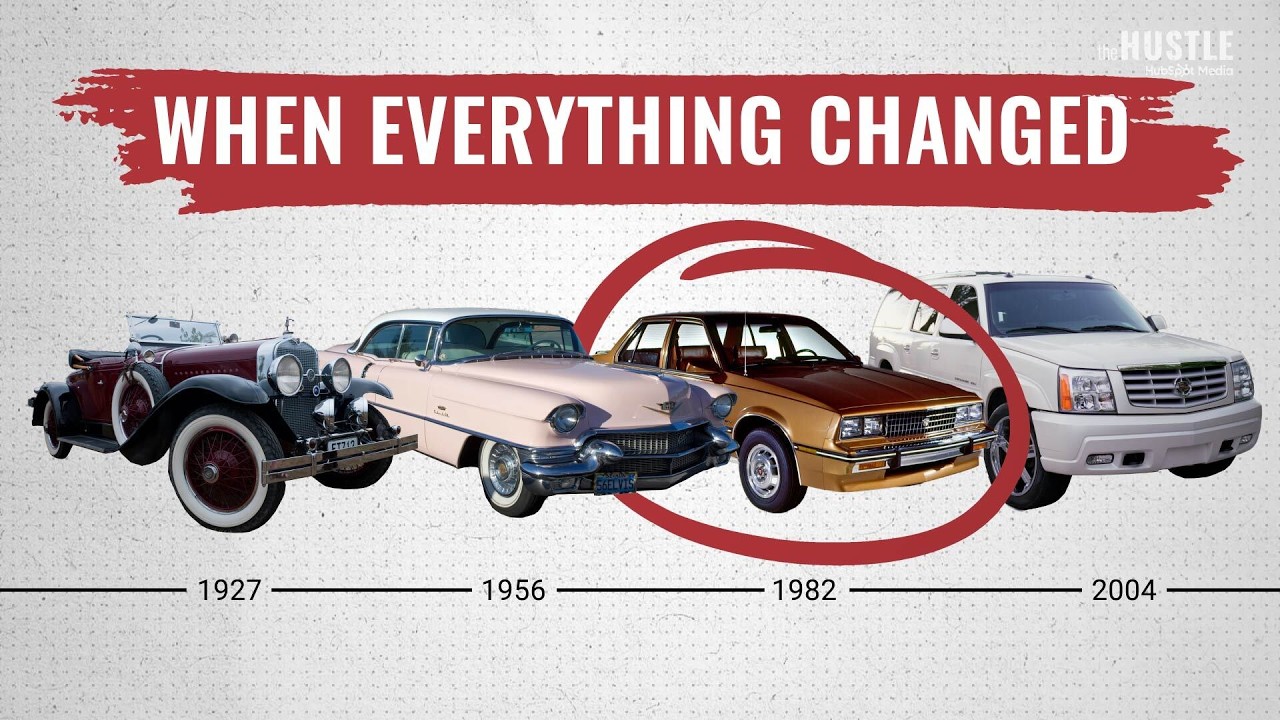
The Rise and Fall of Blockbuster: How an $8b empire vanished
At its peak, Blockbuster Video had over 9,000 stores worldwide, serving 65 million customers a year and making hundreds of millions in profit from late fees alone. So… what happened to Blockbuster?
Comeback Stories
David vs. Goliath
Fresh Ideas
Big Mistakes
Winners vs. The Rest
MBA Refresh
Caribbean
Latest Movies

Ep 32 - From Idea Overload to Execution - A Strategists Guide to Prioritisation
Your organization has 37 brilliant projects. You have bandwidth for maybe 5.
Now what?
This is the reality facing leaders everywhere: expensive master plans that deliver impressive lists of initiatives but zero guidance on which ones to actually pursue. Meanwhile, your CEO expects magic, your budget is maxed out, and that critical board meeting is in two weeks.
Sound familiar?
This episode tackles one of strategy's most brutal challenges: how do you prioritize when everything seems important and resources are painfully limited?
Through the story of "Stephanie"—a VP drowning in a 37-project master plan with no execution roadmap—this conversation exposes the hidden traps of poor prioritization and reveals a systematic approach to cutting through the chaos.
You'll discover:
- Why "let's start everything and see what works" destroys value faster than doing nothing
- The real cost of scattered execution (spoiler: it's not just wasted money)
- A proven framework for organizing idea overload into executable strategy
- How to build decision-driven roadmaps that preserve flexibility while driving focus
- The art of strategic sequencing: when to say "not now" to protect "yes" for the right projects
The hard truth: Most organizations fail not because they lack good ideas, but because they try to execute too many at once. The companies that win? They master the discipline of strategic prioritization.
Stop drowning in possibilities. Start executing with purpose.
🔗 Learn more about opportunity framing: www.wilson.biz
10 Key Timestamps
00:05 - The Idea Overload Problem Why pursuing all your great ideas simultaneously guarantees mediocre results
04:15 - How to Think About Wicked Problems The 55/5 rule: spending most of your time understanding problems, not jumping to solutions
06:38 - The 37-Project Nightmare When your master plan creates more paralysis than clarity
08:48 - The Consultant's Expensive List What happens when deliverables stop short of actual strategic guidance
1:14:10 - The PATH Framework: Organize the Chaos A systematic approach to opportunity framing: Prepare, Analyze, Targets, Handle
1:15:35 - In, Out, or Unknown? The critical distinction that prevents scope creep and forces clarity on uncertainty
1:18:13 - Mapping Your Decision Dependencies Why understanding what choices unlock other choices is the key to sequencing
1:19:38 - Building Strategic Check-In Points Creating moments to pivot before you're too committed to change course
1:21:44 - From Strategy Document to Daily Execution The bridge between high-level plans and operational reality
1:16:33 - The Scope Shuffle Technique How to create space for "I don't know" and turn uncertainty into actionable decisions

The 5-Level Strategic Fluency Ladder

Navigating Innovation and Creating an Invincible Company

Hard to Engage Staff on Vision/Strategy? In Your Sleep w/AI

The Commoncog Method Used by StratCinema

Seeing What's Next: Using Theories of Innovation to Predict

The Dawn and Dusk of Sun Microsystems

The New Long-Term Planning in the Caribbean

Why Strategy Documents Lack Insights
 / chriscfox | https://www.stratnavapp.com/
------- ⏱
Key Chapters: 00:00 - The Problem: Why Most Strategy Docs Are Useless
02:16 - The "Last Year + 10%" Trap (And How to Escape It)
07:38 - Why Brainstorming Alone Fails (And What to Do Instead)
12:45 - How Apple & Amazon Use Insights to Win
18:30 - The Role of AI in Modern Strategy (Beyond Just Automation)
25:10 - How to Build an "Insight Machine" in Your Company
32:50 - Case Study: Turning a Failing Strategy Into a Breakthrough
40:15 - Final Takeaways: How to Stay Ahead in Any Industry
/ chriscfox | https://www.stratnavapp.com/
------- ⏱
Key Chapters: 00:00 - The Problem: Why Most Strategy Docs Are Useless
02:16 - The "Last Year + 10%" Trap (And How to Escape It)
07:38 - Why Brainstorming Alone Fails (And What to Do Instead)
12:45 - How Apple & Amazon Use Insights to Win
18:30 - The Role of AI in Modern Strategy (Beyond Just Automation)
25:10 - How to Build an "Insight Machine" in Your Company
32:50 - Case Study: Turning a Failing Strategy Into a Breakthrough
40:15 - Final Takeaways: How to Stay Ahead in Any Industry 
The Rise and Sad Fall of Wang Labs
📉 The Rise and Tragic Fall of Wang Laboratories
Description
This video details the remarkable entrepreneurial journey and subsequent collapse of Wang Laboratories, founded by the brilliant Chinese immigrant engineer An Wang. The company rose to prominence on the strength of Wang's singular genius, from patenting core memory technology to successfully transitioning from calculators to pioneering word processing systems (WPS) and mini-computers in the 1970s. At its peak, Wang Labs was a Fortune 500 powerhouse, dominating the office automation market. However, the video attributes the company's downfall in the mid-1980s to two critical errors: An Wang's failure to recognize the importance of the IBM PC Revolution and his insistence on appointing his inexperienced son, Fred Wang, to run R&D and later the presidency. This combination of missed technological shifts and chaotic succession led to product delays, internal turmoil, massive financial losses, and ultimately, bankruptcy in 1992, just two years after An Wang's death.
5 Key Moments and Timestamps
-
0:04:39: The Invention of Core Memory - While working at Harvard, An Wang invented the foundational concept for magnetic core memory (an ancestor of RAM) by realizing data could be read and immediately rewritten. He received a patent for this, which he later sold to IBM in 1955 for a crucial $400,000–$500,000 ($4.4M–$5.5M today), providing the seed money to move from consulting to product development.
-
0:12:01: The Calculator Success and Pivot - Wang Labs' first major hit was the Wang 300 calculator (1966), which sold extremely well on Wall Street and helped the company go public in 1967. However, realizing microprocessors would soon commoditize the market, An Wang made the "incredibly ballsy decision" to pull out of the calculator market in 1971 to focus entirely on computers.
-
0:17:19: Dominance with Word Processing - After a failed initial attempt, Wang released the redesigned Wang Word Processing System (WPS) in 1976. It was an immediate hit due to its power, upgradability, and ease of use (ditching IBM's Selectric and using a CRT screen), quickly making Wang the world's largest supplier of CRT-based word processing systems by the late 1970s.
-
0:19:20: Reaching the Peak - In 1978, Wang launched a massive ad campaign, culminating in a Super Bowl ad directly attacking IBM, which boosted public awareness from 3% to 14%. Sales reached $1 billion in 1982 and $2 billion in 1984. An Wang's stake peaked at over $1.6 billion in 1984, making him the richest man in New England.
-
0:24:00: The Fatal Misjudgment - An Wang resisted the PC, believing it was a "dead end commodity" like the calculator. This led him to miss the IBM PC Revolution. Coupled with his decision to install his inexperienced son Fred Wang in critical leadership roles, the company was unable to put out competitive products, leading to a massive 66% quarterly profit decline in 1985 and the beginning of the end.
Jump-Leap Long-Term Strategy Podcast

Recent Episode
Let’s imagine for a moment that you are a citizen or resident of the USA. You love the country and especially the vision of the founding fathers. However, you are distressed by the degree of the political divide. It has hijacked popular attention. People seem to hate each other. Is there a way to find inspiration beyond the current uncertainty? Can leaders possibly come together if only they took a long-term view of the country, and the world?